Blog
A data science blog for Petroleum Engineering.Topics covered
artificial-intelligence
artificial-lift
batch-automation
business-case
cloud
computational-physics
computer-science
conference
courses
data-driven-vs-physics
data-engineering
data-science
data-scientists
data-structures
datasets
deep-learning
engineering-library
fluid-properties
gas-lift
geology
geophysics
geoscience
latex
linux
literate-programming
logs
loose-questions
machine-learning
modeling
open-source-software
paper-research
petroleum-engineering
petrophysics
production-technology
prosper
pvt
python
r
r-package
reproducibility
reservoir-engineering
reservoir-simulation
seismic
shiny
spe
statistics
text-mining
tikz
to-do
transcript
virtualization
visualization-of-data
vlp
volve
webapp
well
well-data
well-logs
well-modeling
Subject ▸ reservoir simulation
Reservoir Simulation Datasets
README Purpose of these datasets is using them for testing using MRST and its derivative Proof of Concept (POC) in Pyhon using the machine learning library PyTorch. Since PyTorch has built-in functionality to work with Graphics Processing Units or GPUs, we expect demonstrating -before embarking in the full porting of MRST-, that PyTorch GPU-based tensors could significantly reduce compute time during reservoir simulation. Evaluation for Proof of Concept The steps are the following:Integrating Python and R for data science. Converting Eclipse binary files to dataframes in the Volve dataset
Introduction Python and R offer a good combination of powers: dozens of proven engineering, data science, and machine learning libraries, also a science oriented approach towards full reproducibility. As I have told you before, I started my coding journey with Python many years ago. I even wrote a large application for production optimization using OpenServer, Prosper, GAP and MBAL by Petroleum Experts while I was on my 3-year tour with Petronas in Kuala Lumpur in Malaysia.A reproducible comparison of the Volve reservoir model
Introduction Continuing with the previous article The fabrication of an artificial intelligence agent for reservoir history matching from the Volve dataset, and the generation of a master dataset for an AI agent to perform history matching of reservoir models, we will extract additional data from the output of the Volve reservoir model, the PRT text file. This is the output “as-is”, as we found it. No additional simulation runs have been performed over this model.The fabrication of an artificial intelligence agent for reservoir history matching from the Volve dataset
Introduction History matching is one of the core activities performed by petroleum engineers to decrease the uncertainty of reservoir models. By comparing real data -production data gathered at the surface-, with the output from a reservoir simulator, the engineer starts filling in the gaps in reservoir properties of those block cells in the model. And this what makes it so interesting in data science, and ultimately, in the fabrication or construction of an artificial intelligence agent.Volve dataset. First look of the Reservoir simulation models.
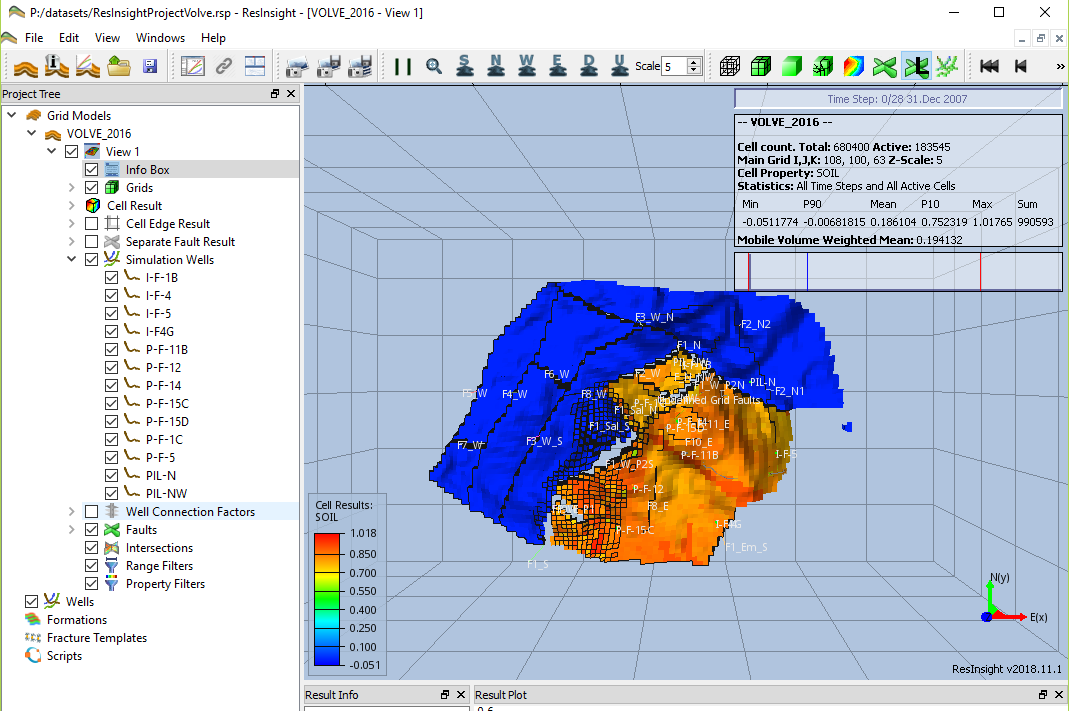
The Eclipse reservoir models from the Volve dataset working like a charm. The compressed file is 399 MB in size.
I was able to open the models with ResInsight (thank you Matthew Kirkman). The software is open source and relatively easy to use.
Here is the Eclipse case opened.
1`